Imagine you’ve been working on a new website for weeks or months, and you’re incredibly happy with the outcome. You were anticipating a good volume of traffic because it is well-designed and informative. Nevertheless, none of that traffic actually happens.
A lot of problems stop search engines from indexing your website. What occurred? Are you hated by Google? Is your website in some way hidden? Have you made a mistake while coding?
Learn how to solve these major challenges so that Google may start indexing your content.
1. Website Is Too New
When a site just went live, Google may occasionally choose not to crawl it. Your website is fine in this instance; Google simply needs some time to crawl and index your webpages.
How much time should Google need to index a new website? The typical waiting period for websites is 4 days to 1 month.
Although some people claim to be indexed more quickly, there is also anecdotal information that indexing can take months.
Solution:
Continue to update and add material to your website.
One outstanding tool is Google Search Console URL inspection tool.
You can request indexing there and input the address of any page on your website or entire domain to view their current index status.
Google will send a bot to your site to crawl and index it, but this is neither a quick remedy nor a guarantee. It could take days, but since it’s so simple and cost-free, why not give it a shot?
2. No Domain Name
Your website will only be reachable by its IP address if it launches without a domain name. Google won’t be able to locate and index it as a result.
The IP name will appear in the address bar in the absence of a domain name.
Solution:
Verify that your URL is configured correctly in WordPress or on the hosting website you use to fix this problem.
You might need to set up 301 redirects to send visitors away from your website’s IP version and to the right version with your domain name.
3. Recent Web Redesign
You can discover that Google hasn’t crawled your website again after revamping, rebranding, or making other big changes.
You must manually submit a recrawl request using Google Search Console if you want to ensure that changes to your website will be reflected in your search engine performance.
If you just made modifications to your website to enhance its crawlability, submitting a recrawl request is extremely beneficial.
Solution:
Make sure your website adheres to the correct rules first.
Examine the URL after that.
Lastly, choose “request indexing.”
As a result, Google will crawl your website once more and index its pages, making them visible in search engine results (SERPs).
3. No sitemap
A sitemap is a systematic list of all the content on your website, including all the pages, videos, files, and links between each piece of content.
If you don’t have this blueprint, Google won’t be able to efficiently crawl and index each of your pages because it contains important information.
Solution:
Ensure to add/install sitemap.
Use an XML sitemap rather than an HTML one to create this file, as the former is optimized for search engine performance.
Once you’ve finished creating your sitemap, you have two options for submitting it to Google: manually through Search Console or by adding a reference to it in your robots.txt file, a plugin that instructs Google which URLs on your site to crawl and index.
4. Your Site Is Not Mobile-Friendly
Since Google adopted Mobile-First indexing, having a mobile-friendly website is essential to getting your site crawled.
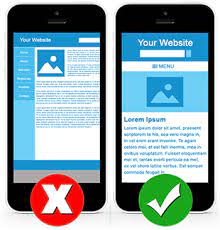
Even if your website has excellent content, you will lose traffic and rankings if it is not optimized for browsing on a smartphone or tablet.
Solution:
By employing adaptive design, reducing the size of images, and enhancing load times, you may make your website more mobile-friendly.
Pop-ups should be eliminated, and finger reach should be considered, which can also help.
Ensure users find what they need without encountering any navigational issues. Try running your site via Google’s Mobile-Friendly Testing Tool.
5. Slow Loading site
Google is less likely to want to highlight slow-loading websites in the top results of their index. There are various reasons why your website can take a long time to load.

It may also be the case that your page contains more content than a user’s browser can handle or that you’re utilizing an outdated server with insufficient resources.
Solution
- Make use of Google Page Speed Insights: This allows you to see which parts of the website need performance optimization the most. The program evaluates your website against five performance best practices, such as limiting connections, lowering payload size, utilizing browser caching, etc. (essential for having quicker running webpages), and provides recommendations for how you can enhance each element of your site.
Also, use the tool called webpagetest.org.
Preferably, your page speed should be at least 70. The optimal solution is to get as close as possible to 100 as you can.
6. Orphan Pages
Google cannot crawl orphan pages on your website, which are pages that are not connected (stand-alone content) to the other pages of your website. Orphan pages can be fixed by being located, then being linked to the rest of your website via internal links.
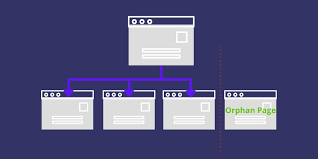
Solution:
You can completely delete an orphan page if it has thin content, or duplicate material, could be interpreted by Google as a doorway page, or if it generally doesn’t provide users with value. In the event that you do this and the orphaned page receives backlinks, implement a 301 redirect to a pertinent Address.
7. Poor Quality Contents
If your webpage content is weak, scraped, or uses keyword stuffing, it may decrease your chances of Google indexing your website because Google wants to give users unique, accurate, and up-to-date search results. Make sure your website is user-centeredly built, offers useful material with applicable keywords, and otherwise conforms to the Webmaster Guidelines in order to address this problem.
Solution
Your website’s content must be worthwhile and informative. Avoid thin content
It must address issues, offer details, or have a viewpoint that is sufficiently distinct from that of other websites in your industry.
Google is constantly looking for relevance and will seek out sites with better content than yours.
If you’re wondering why your website isn’t showing up highly in Google search results for certain keywords despite using best SEO practices.
Remove thin pages, which contain more than just 100 words per page, and ensure your contents are at least 600 words for blogs and 300 words for web pages.
8. Redirect Loops
Redirect loops, or redirects that lead back to themselves, will prevent Google from accurately indexing your pages since the bots become trapped in these loops and are unable to proceed with their crawl of your website. The incorrect type of redirect can also make Googlebot less able to crawl your page.
Solution
Open your website’s HTML sources or your .htaccess file to check for any unintended or improper redirects to rule out this problem.
Correct any errors before using the following redirection code to prevent a duplicate URL address from pointing back at itself:
Google Search Console doesn’t always provide status codes like 404s. You can discover the status codes for 404s and other issues by using an external crawler like Screaming Frog.
For pages that have migrated permanently, 301 redirects should be used; for pages that have moved only temporarily, 302 redirects should be used.
9. The site Isn’t User-friendly To Visitors
A user-friendly and interesting website is essential for effective SEO. If it’s simple for visitors to locate what they’re looking for and navigate the website without feeling frustrated or aggravated, Google will rank your site higher in search results because it has a better user experience.
Google doesn’t want users spending too much time on a page that either takes a very long time to load, has a difficult-to-understand navigation system, or is just difficult to use due to the abundance of distractions.
Solution:
Make sure that every item shown on category pages can be found in its corresponding subcategory so that visitors can simply make purchases without having to navigate challenging linking structures.
10. Using Suspicious or Hard-to-Read Code Complex for Google
Google should be able to access your website’s code with ease, and it should remain fixed between HTML that is displayed and HTML that is raw. Red flags that can stop Google from indexing your website include cloaking or hiding text and links.
Solution
Do not prevent bots from crawling your JavaScript and CSS files To avoid seeming suspicious to Google. Also, if you rely too heavily on JavaScript, Google may not index your website. JavaScript requires more work for bots to understand, which could result in a faster crawl budget burn for your website.
Google will scan and index your website more quickly if questionable or difficult-to-read code is removed.
If you encounter this issue, I advise using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Testing Tool to figure out how really mobile-friendly your website is.
11. Noindex Tag or Header Is Blocking Googlebot
A single line of code can occasionally solve the problem of Google not indexing your website. You’re preventing Google’s crawler bot from accessing your website if your robots.txt file contains the line “User-agent: *Disallow: /” or if you’ve made it difficult for search engines to index your pages in their settings.
Ensure your robots.txt file doesn’t have the following lines:
User-agent: * Disallow: /
The robots.txt file is restricting all pages from the site’s root folder, as indicated by the forward slash.
Solution
- Remove noindex: Google will be unable to crawl and index your website until “noindex” is removed and your page permissions permit search engine visibility.
- You want to make sure that your robots.txt file looks more like this:
User-agent: * Disallow:
12. Incorrect Canonical Tags
When your site has many URLs that display the same or comparable information, canonical tags should be utilized. But, Google will choose for you if you don’t specify which URL you want the search engine to index, which could result in the incorrect version being indexed.
Solution
Check your URLs manually to see if you have canonical issues, or utilize the site audit tools offered by businesses like Ahrefs and Semrush.
13. Crawl budget exceeded
Every website has a set crawl budget, which establishes a numerical cap on the number of pages Googlebot will visit. By accessing the Crawl Stats Report on Google Search Console, you may determine the precise crawl limit for your website.
Google won’t index additional pages on your site if your allotted number has already been reached. The majority of the time, only extremely huge websites are affected by this problem.
Solution
By combining pages following a website audit or by adding code that tells Google not to crawl specific pages on your website, you can fix the problem.
14. Poor Technical SEO
Let’s examine some typical issues, their fixes, and the situations in which technical SEO can be of assistance.
- Problem: Core Web Vitals metrics for your website are not being met.
- Your website has troubles with crawling and indexing.
- The robots.txt file on your website erroneously prevents crawlers from accessing important files.
Solution:
- Technical SEO will assist you in locating problems with your Core Web Vitals and will show you how to fix these problems. Don’t solely rely on a strategic audit; it may not always be of assistance to you in these matters. Some of these problems can range from being incredibly simple to being blatantly simple, so you need a thorough technical SEO audit to find them.
- Get an expert like us to help fix this issue
15. Received a Google Penalty
Check to see if you were penalized by Google. if you can’t figure out why Google isn’t indexing your website based on its content, coding, or usability. Google penalties can be caused by a variety of elements, including harmful websites, sly redirection, and artificial links.
Solution
Log in to Google Search Console to view your penalties. The “Security & Manual Actions” tab should then be selected. There, you can find the essential measures to rectify any penalties that have been filed against your website. Keep in mind Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to prevent further penalties.
Conclusion
Make sure to check off all the boxes and confirm that you are promoting your website in the ideal way.
Remember to optimize each page of your website for relevant keywords as well! The more effectively Google can crawl, index, and rank your site, the better your results will be, therefore it is worthwhile to ensure that your technical SEO is up to snuff.
Do you need help with getting your website indexed by search engines?
To assist you in creating an optimal digital presence, Digiconceptng offers web design, search engine optimization, and content marketing services.
To discover more, contact us right away!