Our SEO checklist post is written to help you execute a comprehensive SEO audit on any site. Learn what’s working, what’s not, and action steps.
An SEO checklist is a comprehensive list of industry best practices that help you optimize any website to perform better in search engine rankings. Doing it right is important and notably, the first step for helping the search engines, rank your site.

The use or the application of Search engine optimization (SEO) has gone beyond what it use to be like keyword stuffing. Now, a lot has been done by Google to rank sites considering different algorithms to enable your site to rank high.
There are over 200 ranking factors used by Google to rank a site on top pages and most of them are secrets but we have been able to highlight and talk about 40 SEO checklist that will improve the way both customers and search engines find and use your website.
Now let us look at 40 SEO Checklist to help you rank on top of SERP
Types of SEO checklist
- Content Optimization
- On-Page Optimization
- Local Optimization
- Mobile Optimization
- Sitewide Optimization
- Server Optimization (NEW)
- Webmaster Tools
Content Optimization
A report or post from Google confirmed that Content is one of the top three ranking factors (out of hundreds) that it uses to rank websites/blogs. This means you need to have a content strategy to help you propel your site to the top page. It is a known fact that a proper SEO content strategy is the difference between unique content and good content.
1. Target Audience Research
This is among the important things to do before, during and after writing your content. You need to define who your target audience is, know their pain points. What questions are they asking and what types of queries they might ask Google will help in your keyword research.
Moreso, you will be able to create content that answers those questions and solve their pain points. Once you can understand searchers’ intent, you can tailor your content to help solve their online requests/queries/problems.
2. Keyword Strategy and Research
You need to be strategic with your Keyword research and know that it is an ongoing process. First, identify and understand the focus phrase or two for the topic you want to write about with the aid of tools to make it easier.

The moment you discover the keyword phrase you want to rank for, check it in Google search. View the top results, the “People also ask” questions, and the rest of the search engine results. The search engine results page (SERP) offers you the best clues to the searcher intent for any query. Ensure your content meets searchers’ intent when looking for a more appropriate keyword phrase.
You can use tools like SEOToolSet Keyword Suggestion tool or Google keyword planner or SEMrush to mention but a few.
3. Featured Snippet
Featured snippets are termed as brief excerpts from a webpage that displays in Google’s search results so as to quickly answer a user’s question. It is also known as the answer box. Featured snippet content is automatically pulled from pages that have been indexed by Google. The most common forms of featured snippets are definitions, lists, steps, and tables.
You can get a featured snippet if you provide answers to question-type queries. That area of the SERP, known as Position Zero, has become a significant SEO focus.
You can get featured snippets when you structure the content according to the type of snippet (usually video, text, list or table). Optimize the answer and formatting, whether it’s a table, bulleted list, ordered list, text question-and-answer, or other.
4. Word Count
Many do not know that this is important in ranking too. The amount of content you need on a webpage varies by topic, keyword, competition, and query.
| 3 TYPES OF SEARCH QUERIES Transactional These queries happen when a user intends to buy something now. Searching for the exact brand and model of a product, for instance, suggests the intention to buy. Informational These are research-oriented queries. People often do research in advance of a future transaction. For example, a search for “baby walker” indicates that the searcher may purchase one soon. Navigational Navigational queries help searchers get anywhere, be it online or offline. For example, Looking for a hotel should take the user to that hotel’s website, phone number, and physical address. |
What is the right word length? Technically no laid down the rule to determine an approximate minimum page length, look at the top-ranked URLs for a keyword you’re targeting. How long are those pages?
I recently tried a tool called SEOToolSet® Multi Page Analyzer, it was useful for this form of analysis.
5. Call to Action (CTA)
It is recommended to offer or provide means for users to take an action on your page. Ensure to make such actionable parts easy to do.
Ensure to make your key pages CTA clear. What primary action a visitor can take next.
- On a product page, the call to action (CTA) should be prominent (for example, “add to cart” or “start a free trial”).
- On a service page, the CTA might be “call us” or “get a quote.” Make the CTA clear and easy to select.
- On the homepage, help the visitor to take the next step in your conversion funnel.
Let us share a sample CTA below
Bookmark this SEO checklist for future reference. And if you find it helpful, please consider sharing it!
6. Content Freshness
It is a good practice to periodically review your content (webpages and blog posts) so that the information is up to date.
We pulled this part from Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines (PDF):
“… unmaintained/abandoned ‘old’ websites or unmaintained and inaccurate/misleading content is a reason for a low E-A-T [expertise, authority and trustworthiness] rating.”
7. Static Content on Homepage
The homepage of any website acts as the main part as it passes authority to top pages on your site through internal links. It is also where your audience lands most often when they search for your brand or main products/services. Provide the necessary info on your homepage s it speaks volumes about your brand.
8. Duplicate Content
There are internal duplicate contents and external duplicate contents. The internal may be ignored by search engines but the external can do more harm than good to your ranking.
You can regularly use CopyScape.com to check for duplicate content. If your site appears to have copied content from another source, it’s a low-quality signal to search engines and may cause your site to rank lower. Besides, if other people have copied your content, this could also spell doom from an SEO angle.
If you have duplicate content within your site, such as three URLs with the same content, a search engine will filter out the dupes. Only one will display in results for relevant queries — and the page that Google chooses might not be the page that you want to rank. One option would be to use a “canonical tag” to tell the search engines which version should be indexed.
Read also:
- Budgeting For Digital Marketing
- How to run Instagram Ads step by step guide
- 10 Reasons Why Your Church Needs a Website
- 6 Important Digital Marketing Tips For Startups
- How to Make Money With Web Marketing Strategy
On-Page Optimization
Many atimes, people fail to understand the categories of these things. We recommend that you review your pages from home to other pages for the following issues below:
9. Title Tag
A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. A page’s title tag is displayed as part of the search snippet in a search engine
Ensure that each page’s meta title is unique and describes the most important information about that page. Use the research keywords and it is roughly 60–70 characters including spaces. (Tip: You can use a title preview tool to estimate how much will show.)
Remember, the title tag often becomes the clickable title that searchers see in search results (though Google reserves the right to choose a different title for your result). Both the title and description text can influence click-throughs to your site. Hence, use compelling tags.
10. Description Tag
The meta description is the small excerpt that appears underneath a website on the SERP that includes information about the page. It is designed to provide users with a brief summary of the content on the page so that users know if the page will answer their questions or not.
Try to include the most important information and keywords near the beginning of your meta description. It usually includes approximately 24 words or 160 characters with spaces.
In recent Google, article releases Google indicates that it does not consider the meta tag an important ranking factor. But look at it this way, anything that appears on a Google SERP page is important. It helps to get clicks.
Do note that Google reserves the right to replace your meta description text with a search snippet generated by Google, which is pulled from the page’s body content. Sometimes, a search snippet shows instead of your meta description whenever Google deems the snippet of text more relevant for a given search. This is common when your description does not contain the query keyword.
11. Heading Tags
Headings give visual clues to how content is organized. It also signals to search engines and readers what topics are covered on a page.
The technical thing to ensure is that the first heading tag within the body of a page is an <h1>. (Note that in WordPress, the text field at the top of the editor that says “Add Title” is actually for the Heading 1.) The following heading tags can be <h2>, <h3>, <h4>, etc., and should be used like a page’s table of contents.
Can I have more than one <h1> on a webpage?
You may have more than one <h1> on a page according to Google, though we recommend only one in most cases. Also, do NOT use heading tags to control font sizes as it may confuse the search engines. Instead, use CSS to control style, and headings to describe the content organization.
Navigation elements and other global text should be styled with CSS and not heading tags.
12. Image Optimization
Images have been known to greatly enhance web pages. The use of images is to enhance/break up the content text and keep a reader interested.
Google AI has improved and can now read images even without the use of alt tags. It offers additional ranking opportunities through image searches and blended web search results.

One thing to note here is that images can slow down a web page’s loading time apart from making it beautiful. You need to reduce file size so as to increase the speed of the page.
When you reduce the image size by approximately 50%, it seriously improves SEO by decreasing page size and speeding page loads.
File names should describe the image and include a keyword when possible. You can also optimize the caption and the text surrounding an image to reinforce what the image is about.
See more on optimizing images for SEO in our post Image SEO – How To Optimize Images for Search
13. Alt Attributes
ALT tag has the alternative text for an image or a visual on a web page. It is one of the fields that can be filled out in your HTML code and enables you to add a description of the picture or video if it is not properly displayed on the screen.
According to Google, having alt attributes is a primary indicator that your site is accessible. Ensure that your images have accurate alt text.
14. Video Optimization
Videos add engagement interest to keep visitors on your page longer. It gives additional SEO benefits and social sharing opportunities to your page. Besides, video is one of the formats for featured snippets in the SERP.
Video content offers ranking chances in regular searches and in video-only search engines where they’re uploaded, especially YouTube.
15. Structured Data Markup with Schema
Structured data clarifies for the search engine what content on your page is about. Specifically, marking up your HTML content based on the standards at schema.org helps the search engines understand what type of information you’re presenting.
For example, you could use structured data markup to indicate an upcoming event your business is hosting, specifying its date, time, location, and other details. If Google is clear about what’s what on your site, then additional bits of information have the potential to show up in your search results.
For example:
- HowTo Article Structured Data – Use this to identify how-to articles.
- FAQ Structured Data – Mark up a Q&A section with this type of schema.
Google’s guidelines allow three supported formats for marking up a website:
- JSON-LD (recommended)
- Microdata
- RDFa
You can check your page or code snippet using Google’s Rich Results Testing Tool.
16. More Structured Data
Here are the other ways you can structure your data for search engines.
- HTML tables
- Bulleted lists
- Ordered lists
- Breadcrumb navigation
- Table of contents at the top (especially with anchor links)
- Headings that contain a key term or question, followed by the answer in body text
- TL;DR (“too long, didn’t read”) summary near the top of your article
This is to help people read your content more easily. It also encourages Google to use your content in featured snippets.
17. Social Meta Tags
Social meta tags or social markup are used to enhance content on social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Pinterest. It helps dictate what image and text will show up when someone shares the link to your content on a social network. This may not be important for SEO but social mentions about your pages are believed to at least temporarily assist with rankings.
You can know more about each platform:
- Facebook Open Graph tags
- Twitter Cards
- Pinterest Pins in various formats
- LinkedIn shares
18. URL Optimization
To optimize your url, avoid underscores rather use dash ( hyphens) in your page URLs. This also should not be used many times to avoid looking spammy. In the olden days, keyword stuffing the URL use to help but now it has minimum or no impact on SEO ranking.
Also make your URLs to be descriptive and contain keywords, without being spammy. You need to know that shorter URLs are preferable to long URLs.
19. Fully Qualified Links
For your links to be read by almost all search engines and not cause crawl issues for some search engines., make your internal links fully qualified. Avoid “../../postname”. Start links with https:// and ensure your sitemap always has fully qualified URLs.
20. Make JavaScript and CSS External
The best practice is to use external scripts and external CSS codes. Using external large files format, it can speed up your page load time as this is an important factor in Google’s ranking algorithm.
In some cases, Google recommends keeping smaller CSS or JavaScript code elements inline in your HTML page as this may help reduce the longer time it may take for the server to request and serve the external resource.
Local Optimization
We have a few important local SEO checklist items.
21. Claim Google My Business Listing
Local SEO is the practice of optimizing a website in order to increase traffic, leads and brand awareness from local search. Common tasks include finding local keywords, optimizing a business’s Google My Business profile, and building “NAP” citations. NAP means Name, Address, and Phone number.
A Google My Business listing is a free tool by Google for businesses with service areas. A Google My Business listing can enable your site to show up in Google Maps, the local pack of Google Search results, and Knowledge Graph panels for your business. Since the goal of SEO is to send traffic to your site from search engines, these appearances are important as SEO items.
There’s a lot more involved in local SEO, but claiming your listing in Google My Business and in Bing Places gets you started.
22. Local Schema Markup
Local schema markup is used to tell the search engines what specific information the site contains and where it is located.
There is a list from Bruceclay on local search ranking factors to help explain this further.
23. Local Citations and Links
This is usually found in directories where multiple businesses are listed either by business type or by region. At a minimum, an online citation should include the business name, address and phone number (NAP) as well as the website address. Many directory sites offer you the luxury of additional business information.
Local links are different from citations in that they exist on local websites, such as related businesses in the area or hyper-local blogs about the area, rather than on a directory. Both the citations and local links help establish your local presence.
Mobile Optimization
Ensure that your website is mobile optimized. It must be responsive and offer a good mpbile browsing experience (UX).
In a recent study, it was discovered that Google looks at the mobile version of your content when it comes to indexing and ranking. Note that Google spider is only concerned with mobile formatting, and that is how your site is viewed.
24. Mobile Usability
Usability for mobile is more about how it feels and behaves than how it looks. You can use the Google search console to know if the touch elements are too close or if the content is sized to the viewport, your Flash usage, font size and more.
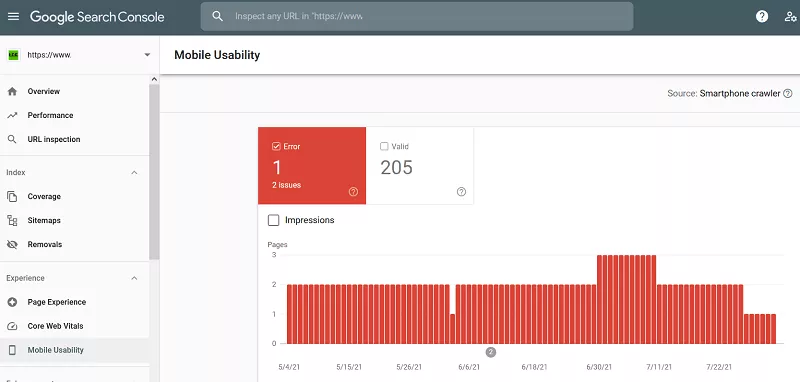
With the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console, you can understand the way Google sees a specific page rendered on different mobile devices.
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test for developers can help you run important URLs checks. Bing offers a Mobile Friendliness Test Tool too to help check or inspect URLs too.
Another important ranking factor is the Page load speed.
25. Mobile and Voice-Related Keywords
This may come as a surprise but it is gradually evolving though not rampant but with time it will become a norm.
You can test if your keywords are easily pronounced?
Keyword recognition is an important part of a query, and the wrong query throws off SEO data.
26. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
Accelerated Mobile Pages, known as AMP is an open-source project that enables web pages to load almost instantly for mobile users.
Google gives cognizance to sites with AMP and they may get more visibility in the mobile search results. We strongly recommend that you avoid AMP unless your site serves audiences in low-bandwidth areas of the world.
Server / HTML Optimization
Google in its recent update considering page experience now considers Core Web Vitals, server-level optimization as a priority.

27. HTTPS
Formerly it used to be a minor ranking factor but now it is part of the page experience ranking factor. It is now a must to serve your site in HTTPS which is secure than the unsecure (HTTP).
Now users can likely see a warning in their browser whenever they try to visit your site. So if you want traffic and rankings, you need a secure site.
Recently we discovered it is good to consider moving your site into HTTP/3. This protocol allows sites to be better optimized for performance. Although it is still a work in progress most browsers and content networks already support it.
28. No Intrusive Interstitials
Intrusive interstitials are pop-ups that get in a user’s way by covering up too much of a webpage soon after the user arrives. Avoid this as it affects Google’s page experience. If you will serve pop-ups, ensure to wait for at least 20–30 seconds after the page is opened before serving such intrusive interstitials.
29. Core Web Vitals
The Google ranking algorithm can be influenced by Core Web Vitals. The metrics used are LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), FID (First Input Delay) and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift), which basically measure how easily people can view and interact with your webpage.
You can check your scores per page using the Core Web Vitals Report in Search Console among other tools.
30. Server Configuration & Maintenance
Lookout for 404 errors, improper 301 redirects and other errors. Involve the use of Google Search Console to point out errors to be fixed.
Server configuration also impacts site speed. As speed is a significant SEO issue. Run Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool and work on the recommended fixes.
Server maintenance takes into count things like plugin maintenance and themes. Safe browsing is a priority even if Google decided to drop it as a page experience ranking factor.
31. Site Speed and Performance
You can analyze and improve your website’s performance on desktop and mobile devices by using PageSpeed Insights in Google Search Console or GTmetrix.com.
Sitewide Optimization
Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines introduced the terminology E-A-T to the SEO community. This stands for expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness as the top indicators of page quality. The E-A-T has now become a cornerstone for search engine optimization.

To rank better, your site should signal expertise, authority and trust while conveying subject relevance and optimizing for search engine accessibility. This is dependent on your content strategy.
32. Contact Information
Did this come as a surprise to you? Well, do not be. Provide your business contact information, such as a phone number and physical address to be visible on your site. The search engines want a trustworthy site to provide a contact for users so as to be found easily.
33. Testimonials
Testimonials if found on your site support your trustworthiness as a business and your value to your customer.
Ensure that your testimonials and reviews are crawlable to be indexed. Try to display them in text (not just images) for search robots to index. Schema markup allows review ratings to be displayed, extending SEO value by increasing traffic.
34. Privacy Statement
A privacy statement lets site visitors know what you’re doing with any data you collect about them.
Put your privacy link in your footer to the privacy page.
35. Text Navigation
Involve the use of text links. Text links are more SEO-friendly than using images for menu items. If you use image menus, it might pose a hindrance to search engine accessibility.
It is recommended to use breadcrumbs with their schema markup throughout your site. Try replacing “Home” in the breadcrumb with a top-level keyword appropriate to your homepage.
36. Sitemaps
Ensure to have both HTML sitemap (see Google’s sitemap info) and XML sitemap that you submit to search engines. Every page should link to that sitemap, probably in the footer.
Websites on WordPress can have their sitemaps updated automatically with the use of plugins Yoast SEO, Rank Math SEO, All in one SEO and so on. You can also check and update them regularly to make sure they contain the pages that are currently active on your site.(For HTML sites)
37. Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file directs the search engine spiders on what not to index. It’s important that this file exists, even if it’s empty. Ensure the file doesn’t accidentally exclude important files, directories, or the entire site.
One important item in this file is the locator for your XML sitemap file. We encourage you to actually have a reasonable robots.txt file.
38. Linking Strategy
Build your internal linking structure from your siloing strategy as it is important to establish relevance for SEO.
Besides, your inbound/outbound links should be part of an organic, natural strategy in compliance with search engine guidelines. Monitor your link profile regularly to help maintain your site.
39. Static URLs
If you can, please avoid dynamic URLs. If your site has any of the following, consider converting your URLS to static URLs:
- More than two query string parameters
- Dynamic pages that aren’t getting indexed
- A lot of duplicate content getting indexed
You can also use mod_rewrite or ISAPI_rewrite as appropriate to simplify URLs. Rewritten URLs will appear to be static URLs. This tends to be a lot of work but is a surefire way to address this issue. You can also use the canonical tag to tell search engines which page is intended to be indexed as the canonical version.
40. No Spam Tactics
Abide by the Google Webmaster Guidelines and Bing Webmaster Guidelines. Avoid spammy tactics or Black Hat SEO.
Webmaster Tools
You need tools that can help you find out how things are on your site. SEO tools help you know what keywords are in trends.

41. Web Analytics
You need to get the report to analyze how your site is performing. Analytics data is important for SEO purposes. Ensure to set up your analytics and monitor them regularly to find out if the keywords generating traffic are in your keyword list, and if your site is optimized for them.
42. Webmaster Tools Accounts
There are free tools provided by search engines to site owners so they can get insight into how search engines view their sites. Google has a Google search console while Bing Uses Bing Webmaster. These free tools collect data and offer essential reports on issues like what search queries bring traffic to your site, crawl errors you need to fix, and penalty notifications.
43. Manual Penalty Review
It is important to occasionally use the Google Search Console to check for any information or update. If a manual penalty has been issued against you, Google will report it to you within GSC. Ensure to always check the Manual Actions Report and the Search Console message center.
The same goes for Bing. Review the Index Summary chart within the dashboard of Bing Webmaster Tools. If the number of pages for a given site is set at zero, you have been hit with a penalty.
44. Algorithm Updates
A good way to check for Google updates may be to use the Panguin Tool and your traffic levels against some algorithmic updates. In the Google Analytics dashboard, you may check to see drops or rises in search referrer traffic that coincide with known algorithm updates. There may be a manual action notice from Google, this might be that you are affected by a penalty.
RankBrain and machine learning — powered by artificial intelligence technology — are changing the search results. Google changes its algorithm and releases updates regularly and this does not go well with some SEO agencies.
Wrapping it up Recommendations
Quality content is important for any good SEO checklist. Nowadays, Google’s algorithm can detect low-quality content and demote its rankings. Avoid thin content. Create topics that solve problems to show your subject matter expertise, and leverage industry experts when possible.
We have been able to outline some of the basic and important SEO checklists that can help you rank better and grow your expertise level and authoritativeness online.