In the world of computing, two terms that often confuse users are “sleep” and “hibernation.” Both functions serve the purpose of conserving power while not in use, but they work differently and have distinct advantages and disadvantages. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of sleep and hibernation modes in PCs, shedding light on their distinctions and helping you make informed choices for your computer’s power management needs.
What is the Difference Between Sleep and Hibernation in Windows
In the realm of personal computing, there are several power management options that allow users to save energy while keeping their PCs readily available for use. Two commonly used modes are Sleep and Hibernation. Although they might seem similar at first glance, these modes serve distinct purposes and have unique characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the differences between Sleep and Hibernation, shedding light on when and why you should use each one.
Sleep Mode: A Quick Nap for Your PC
Sleep mode, also known as standby mode, is a power-saving state designed to quickly bring your PC back to life while consuming minimal power. When you put your computer into sleep mode, it essentially enters a low-power state where it retains the current state of all your open applications and documents in RAM (Random Access Memory). This allows for rapid resumption of your work when you wake it up.
How Sleep Mode Works
- RAM Retention: As mentioned earlier, the key feature of sleep mode is that it keeps your computer’s RAM powered. RAM is volatile memory, meaning it requires a constant power source to maintain its data. By doing so, your PC can awaken almost instantly.
- Low Power Consumption: Sleep mode uses very little power compared to the active state, making it an ideal choice for short breaks when you plan to return to your work soon.
- Wake-Up Triggers: Your PC can be configured to wake up from sleep mode through various triggers, such as pressing a key on the keyboard, moving the mouse, or even a scheduled task.
Advantages of Sleep Mode
- Instant Resumption: The biggest advantage of sleep mode is the quick recovery of your work without the need to reopen applications and documents.
- Energy Efficiency: Sleep mode conserves energy effectively while allowing your PC to remain ready for use.
Hibernation Mode: A Deep Slumber
On the other hand, hibernation mode is a power-saving state that takes power conservation to the next level. When you hibernate your PC, it saves your current state to the hard drive and completely powers off, consuming no power until you wake it up.
Get TikTok SEO Cheat here
How Hibernation Mode Works
- Data Saved to Disk: Instead of relying on RAM to retain data, hibernation mode writes all the data from RAM to the hard drive, usually in a file called “hiberfil.sys.” This ensures that even if power is completely cut off, your work is safe.
- Zero Power Consumption: Unlike sleep mode, hibernation mode consumes no power while your PC is hibernating. This makes it an excellent choice for extended periods of inactivity.
Advantages of Hibernation Mode
- Zero Power Usage: Hibernation is ideal for situations where you won’t be using your PC for an extended period, such as overnight or during travel.
- Data Preservation: Since hibernation saves your work to the hard drive, it’s more robust against power outages or unexpected shutdowns.
Choosing the Right Mode for You
The decision between sleep and hibernation modes depends on your usage patterns and preferences. Here are some scenarios to help you make an informed choice:
- Frequent Short Breaks: If you take frequent short breaks while working on your PC, sleep mode is your best bet. It allows for quick resumption without waiting for your computer to boot up.
- Extended Inactivity: For times when you won’t be using your computer for an extended period, hibernation mode is the way to go. It maximizes power savings and ensures your work is safe.
- Hybrid Sleep: Some systems offer a “hybrid sleep” mode that combines aspects of both sleep and hibernation. It’s an excellent compromise for those who want quick recovery with added data safety.
How to Put Your Computer In Sleep or Hibernation Mode
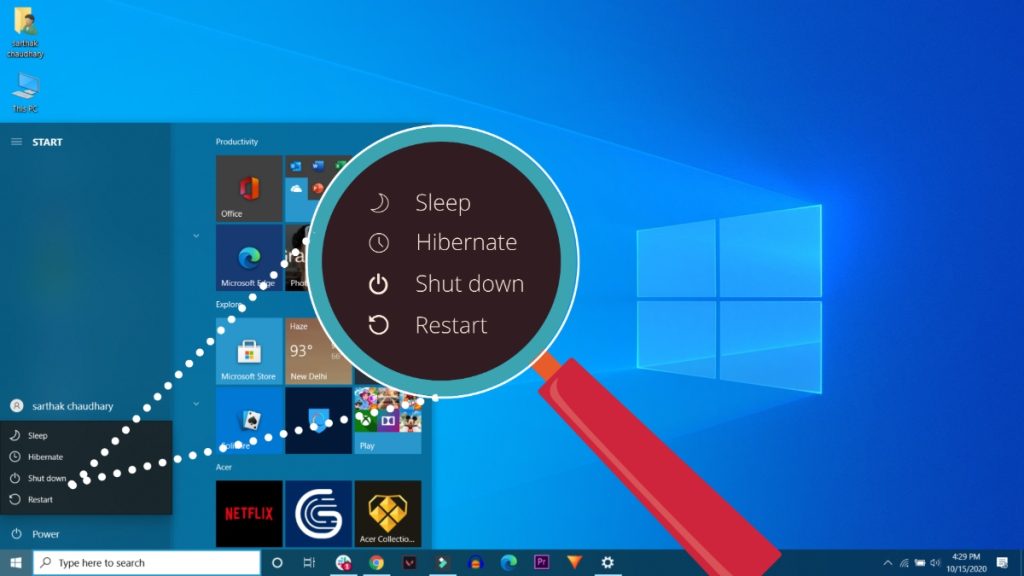
Open your Start menu and select the Power button on Windows 10 or Windows 11 to go to the Hibernate and Sleep choices. The Power menu will include the Hibernate and Sleep options next to others like Shut Down and Restart.
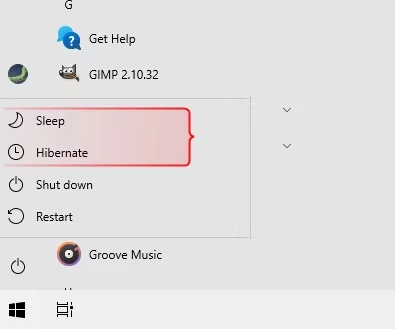
Why can’t i find the Sleep or Hibernation Options?
If you don’t see the Sleep or Hibernate options, one of the following circumstances could be the case:
- Sleep mode might not be supported by your video card. Consult the manual for your video card.
- The driver can also be updated.
- You might need to ask the administrator to update the setting if you don’t have administrative access to the computer.
- Windows’ power-saving modes are enabled and disabled in the BIOS (basic input/output system) of your machine.
- Restart your computer, then use the BIOS configuration application to enable these options.
- For every computer manufacturer, a different key is required to access the BIOS. As the computer boots, instructions for accessing the BIOS typically appear on the screen.
Read also:
- Breaking: Ilebaye wins Big Brother Naija All Stars, ₦120m grand prize
- 4 Reasons Why Ads Do Not Show on the Website
- How Hackers Can Hack Your Info When You Charge Your Devices: Juice Jacking
- How to Find Deleted Texts on Your Husband’s/Wife’s Phone
- 20 Best Free Cooking Apps for Both Nigerian and Foreign Dishes
How to Wake Your Computer from Hibernation or Sleep
The power button on most computers can be used to wake them up. Every computer, though, is unique. You might have to open the laptop lid, click a mouse button, or press a key on the keyboard.
To learn how to wake your computer from a power-saving mode, consult the manual or the manufacturer’s website if you have tried the above in this part.
You may read this:
How to Enable and Disable the Hibernation or Sleep Option in PC
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between sleep and hibernation modes in PCs is crucial for effective power management. While sleep mode provides quick access to your work and conserves energy, hibernation mode ensures zero power consumption and robust data preservation. Choosing the right mode depends on your specific needs and usage patterns.
So, the next time you step away from your PC, consider whether it’s just taking a quick nap (sleep mode) or going into a deep slumber (hibernation mode). Make the choice that best suits your situation, and your PC will thank you for it. Please like and share this for someone in need to know more.